为了讲解redis分布式锁,我将引入一个场景:定时关单。因为往往订单服务是一个集群,那么定时器会同时触发这些集群去取消订单,显然是浪费机器资源的,所以目的是:只让其中一台机器去执行取消订单即可。这里可以用分布式锁来实现。
项目是从练手项目中截取出来的,框架是基于SSM的XML形式构成,所以下面还涉及一点XMl对于定时器spring schedule的配置内容。
1、引入目标
定时自动对超过两个小时还未支付的订单对其进行取消,并且重置库存。
2、配置
首先是spring配置文件引入spring-schedule
1
2
3
4
5
6
| xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task"
...
http://www.springframework.org/schema/task
http://www.springframework.org/schema/task/spring-task.xsd
...
<task:annotation-driven/>
|
补充:针对applicationContext-datasource.xml中的dataSource读取配置文件的信息无法展现的问题,在spring的配置文件中增加一条配置:
1
| <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:datasource.properties"/>
|
3、定时调度代码
此代码的主要功能是:定时调用取消订单服务。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| @Component
@Slf4j
public class CloseOrderTask {
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@Scheduled(cron = "0 */1 * * * ?")
public void closeOrderTaskV1(){
log.info("关闭订单定时任务启动");
int hour = Integer.parseInt(PropertiesUtil.getProperty("close.order.task.time.hour","2"));
orderService.closeOrder(hour);
log.info("关闭订单定时任务结束");
}
}
|
@Component一定要加,否则spring扫描不到。
close.order.task.time.hour 也是配置在snailmall.properties中的,这里配置的是默认的2,即两个小时,下订单超过两个小时仍然不支付,就取消该订单。
对于orderService里面的具体方法:
这里是关单的具体逻辑,细节是行锁。这段代码只要知道他是具体关单的逻辑即可,不需要仔细了解代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| @Override
public void closeOrder(int hour) {
Date closeDateTime = DateUtils.addHours(new Date(),-hour);
List<Order> orderList = orderMapper.selectOrderStatusByCreateTime(Const.OrderStatusEnum.NO_PAY.getCode(),DateTimeUtil.dateToStr(closeDateTime));
for(Order order:orderList){
List<OrderItem> orderItemList = orderItemMapper.getByOrderNo(order.getOrderNo());
for(OrderItem orderItem:orderItemList){
Integer stock = productMapper.selectStockByProductId(orderItem.getProductId());
if(stock == null){
continue;
}
Product product = new Product();
product.setId(orderItem.getProductId());
product.setStock(stock+orderItem.getQuantity());
productMapper.updateByPrimaryKeySelective(product);
}
orderMapper.closeOrderByOrderId(order.getId());
log.info("关闭订单OrderNo:{}",order.getOrderNo());
}
}
|
这样,debug启动项目,一分钟后就会自动执行closeOrderTaskV1方法了。找一个未支付的订单,进行相应测试。
4、存在的问题
经过实验发现,同时部署两台tomcat服务器,执行定时任务的时候是两台都同时执行的,显然不符合我们集群的目标,我们只需要在同一时间只有一台服务器执行这个定时任务即可。那么解决方案就是引入redis分布式锁。
redis实现分布式锁,核心命令式setnx命令。所以阅读下面,您需要对redis分布式锁的基本实现原理必须要先有一定的认识才行。
5、第一种方案

-
第一步:setnx进去,如果成功,说明塞入redis成功,抢占到锁
-
第二步:抢到锁之后,先设置一下过期时间,即后面如果执行不到delete,也会将这个锁自动释放掉,防止死锁
-
第三步:关闭订单,删除redis锁
-
存在的问题:如果因为tomcat关闭或tomcat进程在执行closeOrder()方法的时候,即还没来得及设置锁的过期时间的时候,这个时候会造成死锁。需要改进。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
@Scheduled(cron = "0 */1 * * * ?")
public void closeOrderTaskV2(){
log.info("关闭订单定时任务启动");
long timeout = Long.parseLong(PropertiesUtil.getProperty("lock.timeout"));
Long setnxResult = RedisShardPoolUtil.setnx(Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK,String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()+timeout));
if(setnxResult != null && setnxResult.intValue() ==1){
closeOrder(Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK);
}else {
log.info("没有获取分布式锁:{}",Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK);
}
log.info("关闭订单定时任务结束");
}
private void closeOrder(String lockName) {
RedisShardPoolUtil.expire(lockName,50);
log.info("获取{},ThreadName:{}",Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK,Thread.currentThread().getName());
int hour = Integer.parseInt(PropertiesUtil.getProperty("close.order.task.time.hour","2"));
orderService.closeOrder(hour);
RedisShardPoolUtil.del(lockName);
log.info("释放{},ThreadName:{}",Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK,Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("=============================================");
}
|
6、改进
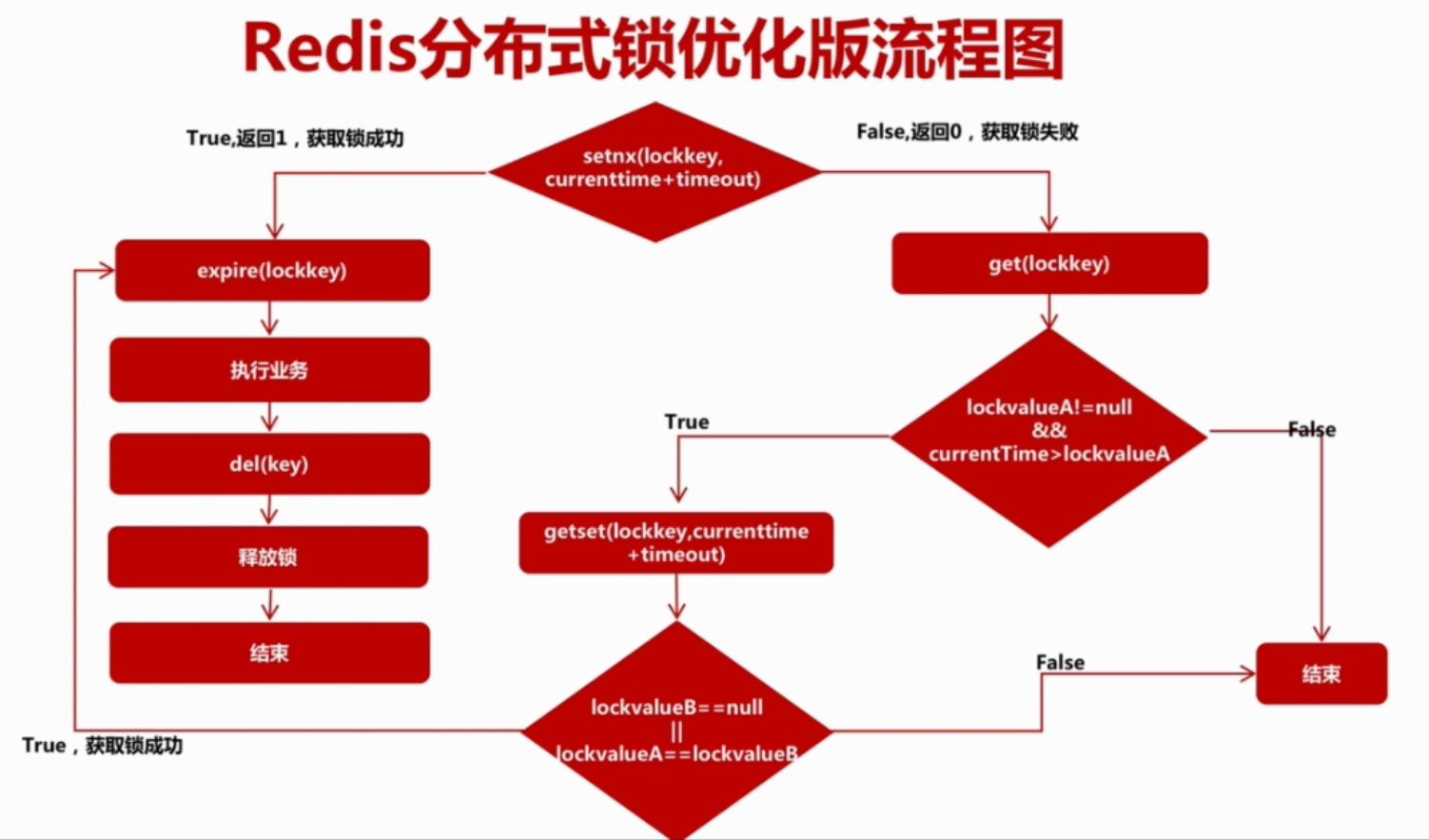
图看不清,可以重新打开一个窗口看。具体的逻辑代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| @Scheduled(cron = "0 */1 * * * ?")
public void closeOrderTaskV3(){
log.info("关闭订单定时任务启动");
long timeout = Long.parseLong(PropertiesUtil.getProperty("lock.timeout"));
Long setnxResult = RedisShardPoolUtil.setnx(Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK,String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()+timeout));
if(setnxResult != null && setnxResult.intValue() ==1){
closeOrder(Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK);
}else {
String lockValueStr = RedisShardPoolUtil.get(Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK);
if(lockValueStr != null && System.currentTimeMillis() > Long.parseLong(lockValueStr)){
String getSetResult = RedisShardPoolUtil.getset(Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK,String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()+timeout));
if(getSetResult == null || (getSetResult != null && StringUtils.equals(lockValueStr,getSetResult))){
closeOrder(Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK);
}else {
log.info("没有获取分布式锁:{}",Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK);
} }else {
log.info("没有获取分布式锁:{}",Const.REDIS_LOCK.CLOSE_ORDER_TASK_LOCK);
}
}
log.info("关闭订单定时任务结束");
}
|
这样两次的防死锁措施,不仅可以防止死锁,还可以提高效率。
7、扩展
mysql四种事务隔离机制
read uncommitted:读取未提交内容
两个线程,其中一个线程执行了更新操作,但是没有提交,另一个线程在事务内就会读到该线程未提交的数据。
read committed:读取提交内容(不可重复读)
针对第一种情况,一个线程在一个事务内不会读取另一个线程未提交的数据了。但是,读到了另一个线程更新后提交的数据,也就是说重复读表的时候,数据会不一致。显然这种情况也是不合理的,所以叫不可重复读。
repeatable read:可重复读(默认)
可重复读,显然解决2中的问题,即一个线程在一个事务内不会再读取到另一个线程提交的数据,保证了该线程在这个事务内的数据的一致性。
对于某些情况,这种方案会出现幻影读,他对于更新操作是没有任何问题的了,但是对于插入操作,有可能在一个事务内读到新插入的数据(但是MySQL中用多版本并发控制机制解决了这个问题),所以默认使用的就是这个机制,没有任何问题。
serializable:序列化
略。
存储引擎
MySQL默认使用的是InnoDB,支持事务。还有例如MyISAM,这种存储引擎不支持事务,只支持只读操作,在用到数据的修改的地方,一般都是用默认的InnoDB存储引擎。
索引的一个注意点
一般类型为normal和unique,用btree实现,对于联合索引(字段1和字段2),在执行查询的时候,例如
1
| select * from xxx where 字段1="xxx" ...
|
是可以利用到索引的高性能查询的,但是如果是
1
| select * from xxx where 字段2="xxx" ...
|
效率跟普通的查询时一样的,因为用索引进行查询,最左边的那个字段必须要有,否则无效。
扩展的内容知识顺便提一下,在数据库这一块,会详细介绍一下。

