10.天气预报系统-集中化配置
这是学习的第十篇文章,服务拆分之后,配置文件就必然随着这些拆分的服务分散在各个服务器上,这对运营是一个灾难,用一个集中化的方式统一进行配置文件的配置与修改是必要的。本章介绍spring config的基本使用,但是还是存在一些小问题,在后面的实战环节中会解决。
一、背景
随着线上项目变的日益庞大,每个项目都散落着各种配置文件,如果采用分布式的开发模式,需要的配置文件随着服务增加而不断增多。某一个基础服务信息变更,都会引起一系列的更新和重启,运维苦不堪言也容易出错。配置中心便是解决此类问题的灵丹妙药。
我们需要一个外部的、集中化的一个配置中心。
二、配置分类
- 按配置的来源划分
主要有源代码、文件、数据库连接、远程调用等
- 按配置的环境划分
主要有开发环境、测试环境、预发布环境、生产环境等。
- 按配置的集成阶段划分
编译时、打包时和运行时
- 按配置的加载方式划分
启动加载和动态加载
三、Spring Cloud Config
在我们了解spring cloud config之前,我可以想想一个配置中心提供的核心功能应该有什么
- 提供服务端和客户端支持
- 集中管理各环境的配置文件
- 配置文件修改之后,可以快速的生效
- 可以进行版本管理
- 支持大的并发查询
- 支持各种语言
Spring Cloud Config可以完美的支持以上所有的需求。
Spring Cloud Config项目是一个解决分布式系统的配置管理方案。它包含了Client和Server两个部分,server提供配置文件的存储、以接口的形式将配置文件的内容提供出去,client通过接口获取数据、并依据此数据初始化自己的应用。Spring cloud使用git或svn存放配置文件,默认情况下使用git.
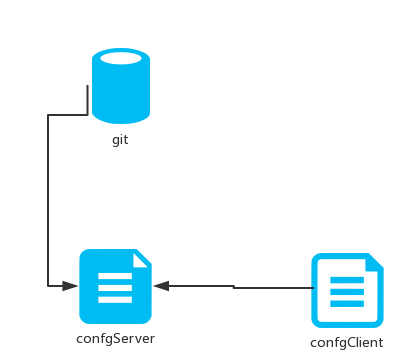
Server端
注册到eureka的实例名:weather-config-server
1、添加依赖
1 | <dependencies> |
2、配置文件
1 | spring: |
config-repo这个文件夹是由自己在github上创建的。在这个目录下新建一个文件:weather-config-client-dev.properties,里面的内容为auther=oursnail.cn(随便写点东西以供测试)
仓库中的配置文件会被转换成web接口,访问可以参照以下的规则:
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
我这里的weather-config-client-dev.properties,它的application是weather-config-client,profile是dev。client会根据填写的参数来选择读取对应的配置。

3、启动类
启动类添加@EnableConfigServer,激活对配置中心的支持
1 |
|
到此server端相关配置已经完成
4、测试
访问 http://localhost:8086/auther/dev 返回:
1 | { |
我们可以读到auther里的内容,说明服务端配置成功。
四、Client端
注册到eureka的实例名:weather-config-client
1、添加依赖
1 | <dependencies> |
2、配置文件
需要配置两个配置文件,application.properties和bootstrap.properties
application.properties如下:
1 | spring.application.name=weather-config-client |
bootstrap.properties如下:
1 | spring.cloud.config.name=weather-config-client |
spring.application.name:对应{application}部分
spring.cloud.config.profile:对应{profile}部分
spring.cloud.config.label:对应git的分支。如果配置中心使用的是本地存储,则该参数无用
spring.cloud.config.uri:配置中心的具体地址,就是server端地址
特别注意:上面这些与spring-cloud相关的属性必须配置在bootstrap.properties中,config部分内容才能被正确加载。因为config的相关配置会先于application.properties,而bootstrap.properties的加载也是先于application.properties。
测试:
1 | (SpringRunner.class) |
如果测试通过,那么获取内容成功。
但是我们通过网页的方式进行测试,我们会发现修改了github上的内容后,网页上的内容是不能立即刷新的。这比较头疼,可以通过一些途径去解决。这个自动刷新问题会在后面的实战项目中实现。
1 |
|