02-分布式文件系统HDFS(一)
从本文开始了解HDFS的基本原理,为后续的实际操作打下理论基础。
HDFS概述及设计目标
如果让我们自己设计一个分布式文件系统,如何来设计呢?可能会简单地这样想:为了保障数据稳定性,那么就可以多存几份,放在不同的节点上,这样,即使某个节点挂了,相应的数据还可以从其他地方读到,如下图所示:
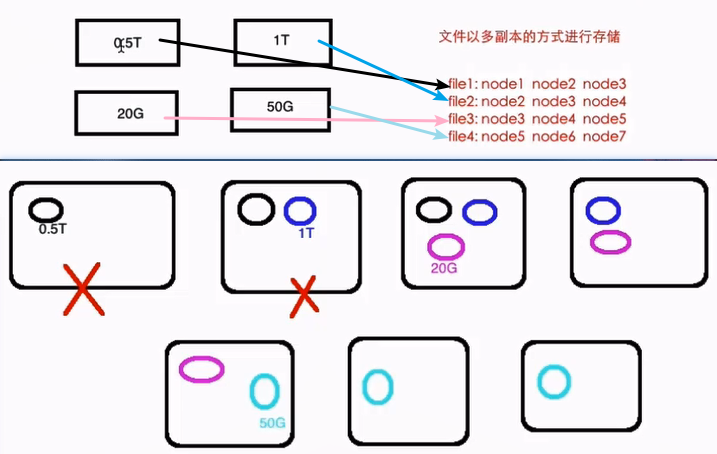
我们看到,这样设计的好处是即使第一个存放数据的节点挂了,也不会有什么影响,后面其他的节点上还是有它的副本的。但是这样设计的缺点也很明显:
- 不管文件多大,都存储在一个节点上,在进行数据处理的时候很难进行并行处理,节点可能就成为网络瓶颈,很难进行大数据的处理
- 存储负载很难均衡,每个节点的利用率很低
HDFS是如何设计的呢?这里简单先说一下,它是先将每个文件进行拆分,默认是128兆,这些拆分出来的block也是多副本进行存储。这样,数据分布会比较均匀,并且可以并行处理,提高并行计算能力。
HDFS设计目标
- 能构建非常巨大的分布式文件系统
- 运行在普通廉价的硬件上
- 易扩展、为用户提供性能不错的文件存储服务
HDFS架构
我们来官网看看HDFS的架构以及说明,其中有一段描述是:
HDFS has a master/slave architecture. An HDFS cluster consists of a single NameNode, a master server that manages the file system namespace and regulates access to files by clients. In addition, there are a number of DataNodes, usually one per node in the cluster, which manage storage attached to the nodes that they run on. HDFS exposes a file system namespace and allows user data to be stored in files. Internally, a file is split into one or more blocks and these blocks are stored in a set of DataNodes. The NameNode executes file system namespace operations like opening, closing, and renaming files and directories. It also determines the mapping of blocks to DataNodes. The DataNodes are responsible for serving read and write requests from the file system’s clients. The DataNodes also perform block creation, deletion, and replication upon instruction from the NameNode.
首先,HDFS是一个主从的架构,包含一个NameNode,它主要负责的是管理namespace以及用户访问的文件;此外,还包含一些DataNodes,主要是负责数据管理。
命名空间的作用:HDFS暴露一个文件系统命名空间允许用户数据保存在这里。NameNode执行系统命名空间操作比如打开、关闭、重命名文件以及目录。这个命名空间还确定了block到DataNode的映射。
DataNode和block:在内部,一个文件是被切割为多个block的,这些block是存储在一系列的DataNode上的。这些DataNode负责提供读写请求,还可以根据NameNode的指令进行block的创建、删除以及复制。
下面总结一下两者的功能:
NameNode(Master/NN):- 负责客户端请求的响应
- 负责元数据(文件的名称、副本系数、block存放的DN)的管理
DataNode(Slaves/DN):- 存储用户的文件对应的数据块(block)
- 要定期向NN发送心跳信息,汇报本身及其所有的block信息,健康状况
官网贴了一张架构图:
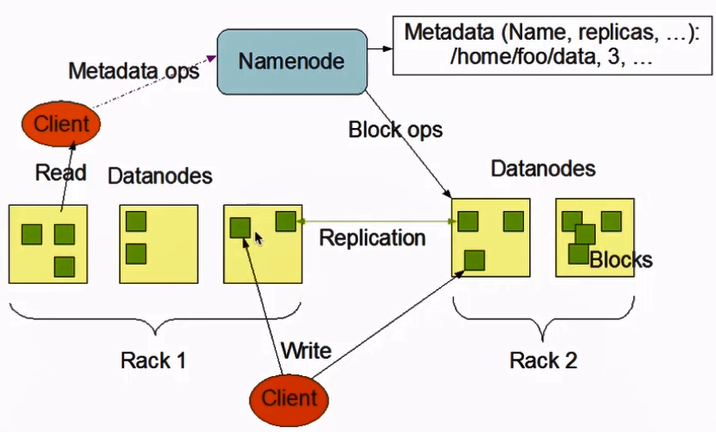
这里感觉有很多东西要额外注意,暂时先学习到这里。
HDFS副本机制
HDFS supports a traditional hierarchical file organization. A user or an application can create directories and store files inside these directories. The file system namespace hierarchy is similar to most other existing file systems; one can create and remove files, move a file from one directory to another, or rename a file.
HDFS支持传统的分层文件组织。 用户或应用程序可以在这些目录中创建目录并存储文件。 文件系统命名空间层次结构与大多数其他现有文件系统类似; 可以创建和删除文件,将文件从一个目录移动到另一个目录,或重命名文件。
The NameNode maintains the file system namespace. Any change to the file system namespace or its properties is recorded by the NameNode. An application can specify the number of replicas of a file that should be maintained by HDFS. The number of copies of a file is called the replication factor of that file. This information is stored by the NameNode.
NameNode维护文件系统名称空间。 NameNode记录对文件系统命名空间或其属性的任何更改。 应用程序可以指定应由HDFS维护的文件的副本数。 文件的副本数称为该文件的复制因子。 该信息由NameNode存储。
HDFS is designed to reliably store very large files across machines in a large cluster. It stores each file as a sequence of blocks. The blocks of a file are replicated for fault tolerance. The block size and replication factor are configurable per file.
HDFS旨在可靠地在集群上存储非常大的文件。 它将每个文件切割为为一系列的块进行存储。这些块被复制成多个副本以达到一定的容错性。 块大小和复制因子可根据文件进行配置。
An application can specify the number of replicas of a file. The replication factor can be specified at file creation time and can be changed later. Files in HDFS are write-once (except for appends and truncates) and have strictly one writer at any time.
应用程序可以指定文件的副本数。 复制因子可以在文件创建时指定,并可以在以后更改。 HDFS中的文件是一次写入的(除了追加和删除),并且在任何时候都有一个在写入,也就是说不支持并发写。
The NameNode makes all decisions regarding replication of blocks. It periodically receives a Heartbeat and a Blockreport from each of the DataNodes in the cluster. Receipt of a Heartbeat implies that the DataNode is functioning properly. A Blockreport contains a list of all blocks on a DataNode.
它定期从群集中的每个DataNode接收Heartbeat和Blockreport。 收到心跳意味着DataNode正常运行。 Blockreport包含DataNode上所有块的列表。
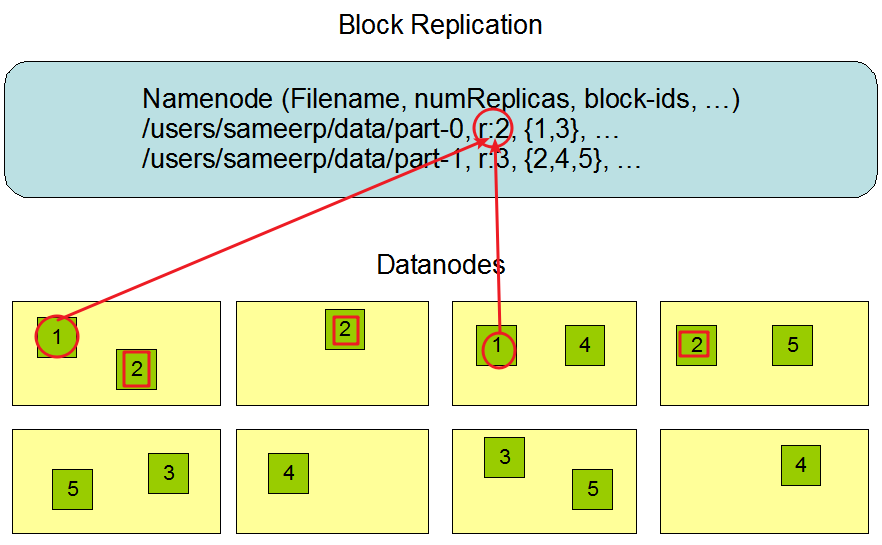
HDFS副本存放策略
为了提高可用性,大型Hadoop集群以机架的形式来组织的,同一个机架上不同节点间的网络状况比不同机架之间更为理想。
那么副本是如何存储呢?
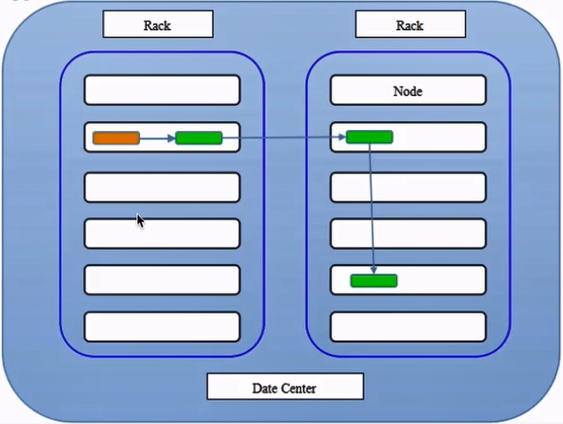
如图所示,这里以默认的三个副本为例子说明,一般策略是这样的:同一个机架的同一台机器上先放一个副本,然后不同机架随机选择两个机器放副本。这样,一旦其中一个机架挂了,另一个机架还可以继续工作。
至此,关于HDFS基础的理论都已经说明完毕了,下面就要来实际操作一把了。